Available on Canopsis
Community and Pro
Active feature
since Canopsis 24.04
With the Root cause feature, implement new state calculation algorithms and identify the root cause of an alarm!
Without the Root cause module:
- the state of a service is equivalent to the worst state of its dependencies
- the state of a component is provided by an event
The Root cause feature lets you add algorithms for calculating service and component states. The state or severity of a service can now depend on state calculation rules applied to its dependencies:
There are two types of rules for state calculation algorithms:
1. Dependencies induce states
Which dependency(ies) of the target entity will be responsible for the final state?
If several dependencies are selected by the model, then the worst state of these will be used.
2. A share or number of dependencies of a specific state define the states
In this mode, it is possible to define the state of a service from conditions based on a percentage or number of states of the service’s dependencies.
We could, for example, express the fact that the service will be in condition
- Critical if more than 50% of its dependencies are in critical condition or
- Major if 3 of its outbuildings are in minor condition or
- Minor if 20% of entities are in major state or
- OK if at least 1 dependency is in OK state
From a dependency diagram of this type :
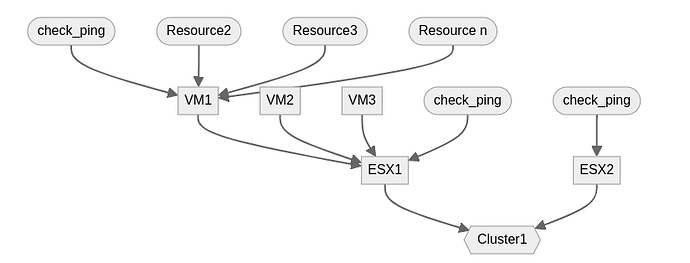
Canopsis can propose a result as follows:
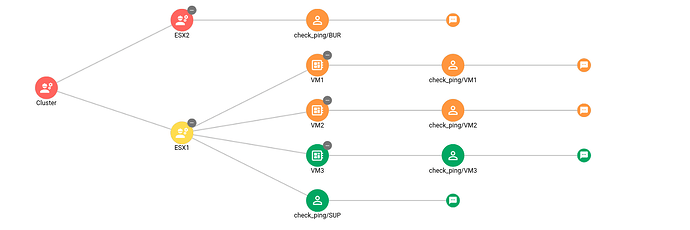
Finally, when no rule applies, the state of the service is equal to the worst state of its dependencies.
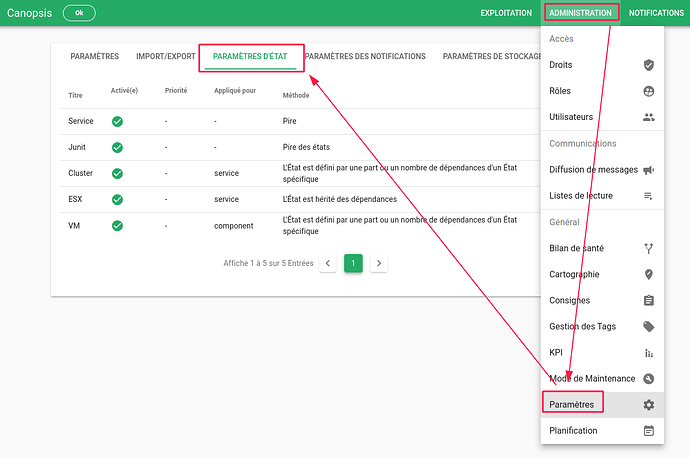
For more information on the Root Cause feature, see the Canopsis documentation.
✅ Update 2024: Root cause feature suggests the reason for one or more incidents
This causality can be determined by two factors:
- The repository
- Manually defined links

Audience
- Supervision pilots
- Application managers

Added value
- Relevance
- Decision support
- Time saving
- Operational efficiency

